前言
当接到可视化大屏需求时,你是否会有以下疑问👇 如何做一款定制化的数据大屏? 开发可视化数据大屏如何做自适应? vm vh、rem、scale 到底哪种比较好? 时间不够,有没有偷懒的方法?
而解决了适配问题后,后面就只是一个慢工出细活,耗时间的事情了。
适配方案分析
看了网上的各种方案,目前大家采用的大概有 3 种👇
| 方案 | 实现方式 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| vm vh | 1.按照设计稿的尺寸,将px按比例计算转为vw和vh | 1.可以动态计算图表的宽高,字体等,灵活性较高 2.当屏幕比例跟 ui 稿不一致时,不会出现两边留白情况 | 1.每个图表都需要单独做字体、间距、位移的适配,比较麻烦 |
| scale | 1.通过 scale 属性,根据屏幕大小,对图表进行整体的等比缩放 | 1.代码量少,适配简单 2.一次处理后不需要在各个图表中再去单独适配 | 1.因为是根据 ui 稿等比缩放,当大屏跟 ui 稿的比例不一样时,会出现周边留白情况 2.当缩放比例过大时候,字体会有一点点模糊,就一点点 3.当缩放比例过大时候,事件热区会偏移。 |
| rem + vm vh | 1.获得 rem 的基准值 2.动态的计算html根元素的font-size 3.图表中通过 vm vh 动态计算字体、间距、位移等 | 1.布局的自适应代码量少,适配简单 | 1.因为是根据 ui 稿等比缩放,当大屏跟 ui 稿的比例不一样时,会出现周边留白情况 2.图表需要单个做字体、间距、位移的适配 |
以上 3 种方案在实际应用中该怎么选择视具体情况而定,也有看到大家说自适应在地图的适配中会有一些兼容问题,我这边还没有实践过。
- 如果想简单,客户能同意留白,选用
scale即可 - 如果需要兼容不同比例的大屏,并且想在不同比例中都有比较好的效果,图表占满屏幕,类似于移动端的响应式,可以采用 vm vh 的方案
- 至于 rem,个人觉得就是 scale 和 vm vh 的综合,最终的效果跟
scale差不多
接下来介绍下三种方案的具体实现,方案中的代码都以 vue2.0 和 vue-cli3 搭建的 vue 项目为例,因为是 demo,图表的一些细节就没有过多细致的调整了
方案一:vw vh
上效果

当屏幕的尺寸比例刚好是 16:9 时
当屏幕的尺寸比例大于 16:9 时
当屏幕的尺寸比例小于 16:9 时
实现思路
按照设计稿的尺寸,将px按比例计算转为vw和vh,转换公式如下
假设设计稿尺寸为 1920*1080(做之前一定问清楚 ui 设计稿的尺寸)
即:
网页宽度=1920px
网页高度=1080px
我们都知道
网页宽度=100vw
网页宽度=100vh
所以,在 1920px*1080px 的屏幕分辨率下
1920px = 100vw
1080px = 100vh
这样一来,以一个宽 300px 和 200px 的 div 来说,其所占的宽高,以 vw 和 vh 为单位,计算方式如下:
vwDiv = (300px / 1920px ) * 100vw
vhDiv = (200px / 1080px ) * 100vh
所以,就在 1920*1080 的屏幕分辨率下,计算出了单个 div 的宽高
当屏幕放大或者缩小时,div 还是以 vw 和 vh 作为宽高的,就会自动适应不同分辨率的屏幕
复制代码话不多说,上代码
css 方案 – sass
util.scss
// 使用 scss 的 math 函数,https://sass-lang.com/documentation/breaking-changes/slash-div
@use "sass:math";
// 默认设计稿的宽度
$designWidth: 1920;
// 默认设计稿的高度
$designHeight: 1080;
// px 转为 vw 的函数
@function vw($px) {
@return math.div($px, $designWidth) * 100vw;
}
// px 转为 vh 的函数
@function vh($px) {
@return math.div($px, $designHeight) * 100vh;
}路径配置 只需在vue.config.js里配置一下utils.scss的路径,就可以全局使用了
vue.config.js
const path = require("path");
function resolve(dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, dir);
}
module.exports = {
publicPath: "",
configureWebpack: {
name: "app name",
resolve: {
alias: {
"@": resolve("src"),
},
},
},
css: {
// 全局配置 utils.scs,详细配置参考 vue-cli 官网
loaderOptions: {
sass: {
prependData: `@import "@/styles/utils.scss";`,
},
},
},
};在 .vue 中使用
<template>
<div class="box">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name: "Box",
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped="scoped">
/*
直接使用 vw 和 vh 函数,将像素值传进去,得到的就是具体的 vw vh 单位
*/
.box{
width: vw(300);
height: vh(100);
font-size: vh(16);
background-color: black;
margin-left: vw(10);
margin-top: vh(10);
border: vh(2) solid red;
}
</style>css 方案 – less
utils.less
@charset "utf-8";
// 默认设计稿的宽度
@designWidth: 1920;
// 默认设计稿的高度
@designHeight: 1080;
.px2vw(@name, @px) {
@{name}: (@px / @designWidth) * 100vw;
}
.px2vh(@name, @px) {
@{name}: (@px / @designHeight) * 100vh;
}
.px2font(@px) {
font-size: (@px / @designWidth) * 100vw;
}路径配置 在vue.config.js里配置一下utils.less
const path = require("path");
function resolve(dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, dir);
}
module.exports = {
publicPath: "",
configureWebpack: {
name: "app name",
resolve: {
alias: {
"@": resolve("src"),
},
},
},
css: {
// 全局配置utils.scss
loaderOptions: {
less: {
additionalData: `@import "@/styles/utils.less";`,
},
},
},
};在 .vue 文件中使用
<template>
<div class="box">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name: "Box",
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped="scoped">
/*
直接使用 vw 和 vh 函数,将像素值传进去,得到的就是具体的 vw vh单位
*/
.box{
.px2vw(width, 300);
.px2vh(height, 100);
.px2font(16);
.px2vw(margin-left, 300);
.px2vh(margin-top, 100);
background-color: black;
}
</style>定义 js 样式处理函数
// 定义设计稿的宽高
const designWidth = 1920;
const designHeight = 1080;
// px转vw
export const px2vw = (_px) => {
return (_px * 100.0) / designWidth + 'vw';
};
export const px2vh = (_px) => {
return (_px * 100.0) / designHeight + 'vh';
};
export const px2font = (_px) => {
return (_px * 100.0) / designWidth + 'vw';
};屏幕变化后,图表自动调整
这种使用方式有个弊端,就是屏幕尺寸发生变化后,需要手动刷新一下才能完成自适应调整
为了解决这个问题,你需要在各个图表中监听页面尺寸变化,重新调整图表,在 vue 项目中,也可以借助element-resize-detector,最好封装个 resize 的指令,在各图表中就只要使用该指令就可以了,毕竟作为程序员,能偷懒就偷懒
- 安装 element-resize-detector
npm install element-resize-detector –save
- 引入工具包在组件中使用或者在单独的 js 中使用
import resizeDetector from ‘element-resize-detector’
- 封装 directive
// directive.js
import * as ECharts from "echarts";
import elementResizeDetectorMaker from "element-resize-detector";
import Vue from "vue";
const HANDLER = "_vue_resize_handler";
function bind(el, binding) {
el[HANDLER] = binding.value
? binding.value
: () => {
let chart = ECharts.getInstanceByDom(el);
if (!chart) {
return;
}
chart.resize();
};
// 监听绑定的div大小变化,更新 echarts 大小
elementResizeDetectorMaker().listenTo(el, el[HANDLER]);
}
function unbind(el) {
// window.removeEventListener("resize", el[HANDLER]);
elementResizeDetectorMaker().removeListener(el, el[HANDLER]);
delete el[HANDLER];
}
// 自定义指令:v-chart-resize 示例:v-chart-resize="fn"
Vue.directive("chart-resize", { bind, unbind });- main.js 中引入
import '@/directive/directive';- html 代码
<template>
<div class="linechart">
<div ref="chart" v-chart-resize class="chart"></div>
</div>
</template>这里要注意的是,图表中如果需要 tab 切换动态更新图表数据,在更新数据时一定不要用 echarts 的 dispose 方法先将图表移除,再重新绘制,因为 resize 指令中挂载到的图表实例还是旧的,就监听不到新的 chart 元素的 resize 了,更新数据只需要用 chart 的 setOption 方法重新设置配置项即可。
图表字体、间距、位移等尺寸自适应
echarts 的字体大小只支持具体数值(像素),不能用百分比或者 vw 等尺寸,一般字体不会去做自适应,当宽高比跟 ui 稿比例出入太大时,会出现文字跟图表重叠的情况
- 默认情况下,这里以你的设计稿是 1920*1080 为例,即网页宽度是 1920px (做之前一定问清楚 ui 设计稿的尺寸)
- 把这个函数写在一个单独的工具文件
dataUtil.js里面,在需要的时候调用 - 其原理是计算出当前屏幕宽度和默认设计宽度的比值,将原始的尺寸乘以该值
- 另外,其它 echarts 的配置项,比如间距、定位、边距也可以用该函数
- 编写 dataUtil.js 工具函数
// Echarts图表字体、间距自适应
export const fitChartSize = (size,defalteWidth = 1920) => {
let clientWidth = window.innerWidth||document.documentElement.clientWidth||document.body.clientWidth;
if (!clientWidth) return size;
let scale = (clientWidth / defalteWidth);
return Number((size*scale).toFixed(3));
}- 将函数挂载到原型上
import {fitChartSize} from '@src/utils/dataUtil.js'
Vue.prototype.fitChartFont = fitChartSize;- 这样你可以在
.vue文件中直接使用this.fitChartSize()调用
<template>
<div class="chartsdom" ref="chart" v-chart-resize></div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "dashboardChart",
data() {
return {
option: null,
};
},
mounted() {
this.getEchart();
},
methods: {
getEchart() {
let myChart = this.$echarts.init(this.$refs.chart);
const option = {
backgroundColor: "transparent",
tooltip: {
trigger: "item",
formatter: "{a} <br/>{b} : {c}%",
},
grid: {
left: this.fitChartSize(10),
right: this.fitChartSize(20),
top: this.fitChartSize(20),
bottom: this.fitChartSize(10),
containLabel: true,
},
calculable: true,
series: [
{
color: ["#0db1cdcc"],
name: "计划投入",
type: "funnel",
width: "45%",
height: "70%",
x: "5%",
minSize: "10%",
funnelAlign: "right",
center: ["50%", "50%"], // for pie
data: [
{
value: 30,
name: "下单30%",
},
{
value: 55,
name: "咨询55%",
},
{
value: 65,
name: "点击65%",
},
{
value: 60,
name: "访问62%",
},
{
value: 80,
name: "展现80%",
},
].sort(function (a, b) {
return a.value - b.value;
}),
roseType: true,
label: {
normal: {
formatter: function () {},
position: "inside",
},
},
itemStyle: {
normal: {
borderWidth: 0,
shadowBlur: this.fitChartSize(20),
shadowOffsetX: 0,
shadowOffsetY: this.fitChartSize(5),
shadowColor: "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3)",
},
},
},
{
color: ["#0C66FF"],
name: "实际投入",
type: "funnel",
width: "45%",
height: "70%",
x: "50%",
minSize: "10%",
funnelAlign: "left",
center: ["50%", "50%"], // for pie
data: [
{
value: 35,
name: "下单35%",
},
{
value: 40,
name: "咨询40%",
},
{
value: 70,
name: "访问70%",
},
{
value: 90,
name: "点击90%",
},
{
value: 95,
name: "展现95%",
},
].sort(function (a, b) {
return a.value - b.value;
}),
roseType: true,
label: {
normal: {
position: "inside",
},
},
itemStyle: {
normal: {
borderWidth: 0,
shadowBlur: this.fitChartSize(20),
shadowOffsetX: 0,
shadowOffsetY: this.fitChartSize(5),
shadowColor: "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3)",
},
},
},
],
};
myChart.setOption(option, true);
},
},
beforeDestroy() {},
};
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.chartsdom {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>方案二:scale
通过 css 的 scale 属性,根据屏幕大小,对图表进行整体的等比缩放,从而达到自适应效果
上效果

当屏幕的尺寸比例刚好是 16:9 时,页面能刚好全屏展示,内容占满显示器
当屏幕的尺寸比例小于 16:9 时,页面上下留白,左右占满并上下居中,显示比例保持 16:9
当屏幕尺寸比例大于 16:9 时,页面左右留白,上下占满并居中,显示比例保持 16:9
话不多说,上代码
html 部分
<div className="screen-wrapper">
<div className="screen" id="screen">
</div>
</div>js 部分
<script>
export default {
mounted() {
// 初始化自适应 ----在刚显示的时候就开始适配一次
handleScreenAuto();
// 绑定自适应函数 ---防止浏览器栏变化后不再适配
window.onresize = () => handleScreenAuto();
},
deleted() {
window.onresize = null;
},
methods: {
// 数据大屏自适应函数
handleScreenAuto() {
const designDraftWidth = 1920; //设计稿的宽度
const designDraftHeight = 960; //设计稿的高度
// 根据屏幕的变化适配的比例
const scale =
document.documentElement.clientWidth /
document.documentElement.clientHeight <
designDraftWidth / designDraftHeight
? document.documentElement.clientWidth / designDraftWidth
: document.documentElement.clientHeight / designDraftHeight;
// 缩放比例
document.querySelector(
'#screen',
).style.transform = `scale(${scale}) translate(-50%, -50%)`;
},
},
};
</script>css部分
/*
除了设计稿的宽高是根据您自己的设计稿决定以外,其他复制粘贴就完事
*/
.screen-root {
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
.screen {
display: inline-block;
width: 1920px; //设计稿的宽度
height: 960px; //设计稿的高度
transform-origin: 0 0;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: -50%;
}
}实现思路
如何缩放
当屏幕宽高比 < 设计稿宽高比,我们需要缩放的比例是屏幕宽度 / 设计稿宽度 当屏幕宽高比 > 设计稿宽高比,我们需要缩放的比例是屏幕高度 / 设计稿高度
const scale = document.documentElement.clientWidth / document.documentElement.clientHeight < designDraftWidth / designDraftHeight ?
(document.documentElement.clientWidth / designDraftWidth) :
(document.documentElement.clientHeight / designDraftHeight);如果我们拿到的设计稿宽高为: 1920 * 960 px ,而我们的屏幕大小是 1440 * 900 px,那么 1440/900 = 1.6,920/960 = 2
因为 1.6 < 2 (当前屏幕宽高比小于设计稿宽高比)
所以我们需要缩放的比例是:屏幕宽度除以设计稿宽度 = 1440/1920 = 0.75
如何居中 首先我们利用 transform:translate(-50%,-50%) ,将动画的基点设为左上角
transform-origin:设置动画的基点(中心点),默认点是元素的中心点
语法
transform-origin: x-axis y-axis z-axis;
然后利用transform:translate(-50%,-50%),将图表沿 x,y 轴移动 50%
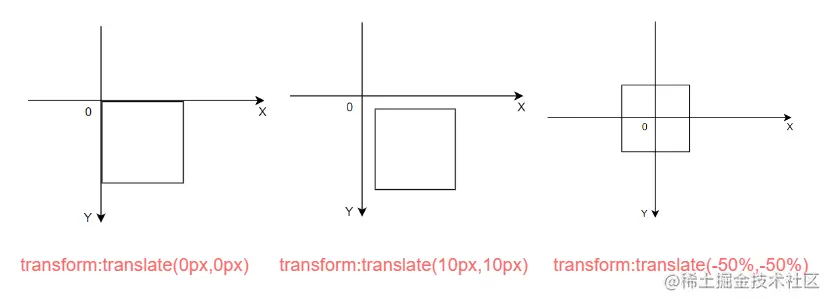
接下来利用绝对定位将图表定位到中间位置
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
复制代码偷懒方法-插件
v-scale-screen是使用 css 属性 transform 实现缩放效果的一个大屏自适应组件,通过 scale 进行等比例计算,达到等比例缩放的效果,同时也支持铺满全屏,宽度等比,高度等比,等自适应方案,具体可查大屏自适应终极解决方案
方案三:rem + vw wh
上效果
当屏幕的尺寸比例刚好是 16:9 时,页面能刚好全屏展示,内容占满显示器
当屏幕的尺寸比例小于 16:9 时,页面上下留白,左右占满并上下居中,显示比例保持 16:9
当屏幕尺寸比例大于 16:9 时,页面左右留白,上下占满并居中,显示比例保持 16:9
实现思路
关于 rem rem(font size of the root element),是 css3 中新增的一个大小单位,即相对于根元素 font-size 值的大小。 自适应思路 动态的计算出页面的 fontsize 从而改变 rem 的大小。
- 拿 1920 * 1080 的标准屏幕大小为例,将屏幕分为
10份,先计算rem 的基准值:1920 / 10 = 192; - 把所有元素的长、宽、位置、字体大小等原来的 px 单位全部转换成 rem;
因此 rem + vm vh 方案要解决三件事
- 获得 rem 的基准值;
- 页面内写一段 js 代码,动态的计算
html根元素的font-size; - 屏幕变化后,图表自动调整和图表字体、间距、位移等的自适应。
实现方案
第一点:获得 rem 的基准值
- 首先安装
@njleonzhang/postcss-px-to-rem这个包
npm i @njleonzhang/postcss-px-to-rem -D- 在项目根目录新建
.postcssrc.js配置文件
module.exports = {
plugins: {
autoprefixer: {},
"@njleonzhang/postcss-px-to-rem": {
unitToConvert: 'px', // (String) 要转换的单位,默认是 px。
widthOfDesignLayout: 1920, // (Number) 设计布局的宽度。对于pc仪表盘,一般是 1920.
unitPrecision: 3, // (Number) 允许 rem 单位增长到的十进制数字.
selectorBlackList: ['.ignore', '.hairlines'], // (Array) 要忽略并保留为 px 的选择器.
minPixelValue: 1, // (Number) 设置要替换的最小像素值.
mediaQuery: false // (Boolean) 允许在媒体查询中转换 px.
}
}
}- 配置完成后,页面内的 px 就会被转换成 rem 了
第二点:动态的计算html根元素的font-size
- 在工具函数文件中新建一个 rem.js 文件,用于动态计算 font-size
(function init(screenRatioByDesign = 16 / 9) {
let docEle = document.documentElement
function setHtmlFontSize() {
var screenRatio = docEle.clientWidth / docEle.clientHeight;
var fontSize = (
screenRatio > screenRatioByDesign
? (screenRatioByDesign / screenRatio)
: 1
) * docEle.clientWidth / 10;
docEle.style.fontSize = fontSize.toFixed(3) + "px";
console.log(docEle.style.fontSize);
}
setHtmlFontSize()
window.addEventListener('resize', setHtmlFontSize)
})()- 在入口文件 main.js 中引入 rem.js 文件
import './utils/rem.js';至此,页面就已经可以实现 16:9 自适应了。
第三点:屏幕变化,图表自适应 屏幕变化后,图表自动调整字体、间距、位移等,此处参考上面 vm vh 的实现方式即可,在此就不重复赘述了
参考资料
- 推荐一个echarts 的案列网站,需要什么直接图表直接在上面去找,可以省去很多查 echarts 配置的时间 全网echarts案例资源大总结和echarts的高效使用技巧(细节版)
- scale 方案参考: 数据大屏最简单自适应方案,无需适配rem单位
- vm vh 方案参考: Vue+Echarts企业级大屏项目适配方案
- rem 方案参考:数据大屏rem适配方案

 UI树欲静
UI树欲静

